US Dollar dips with ADP, S&P Global and ISM data all painting mixed picture

- The US Dollar looks unable to recover earlier losses this Wednesday against most major peers on Wednesday.
- Despite upbeat ADP and S&P Global PMI data, ISM data contradicts.
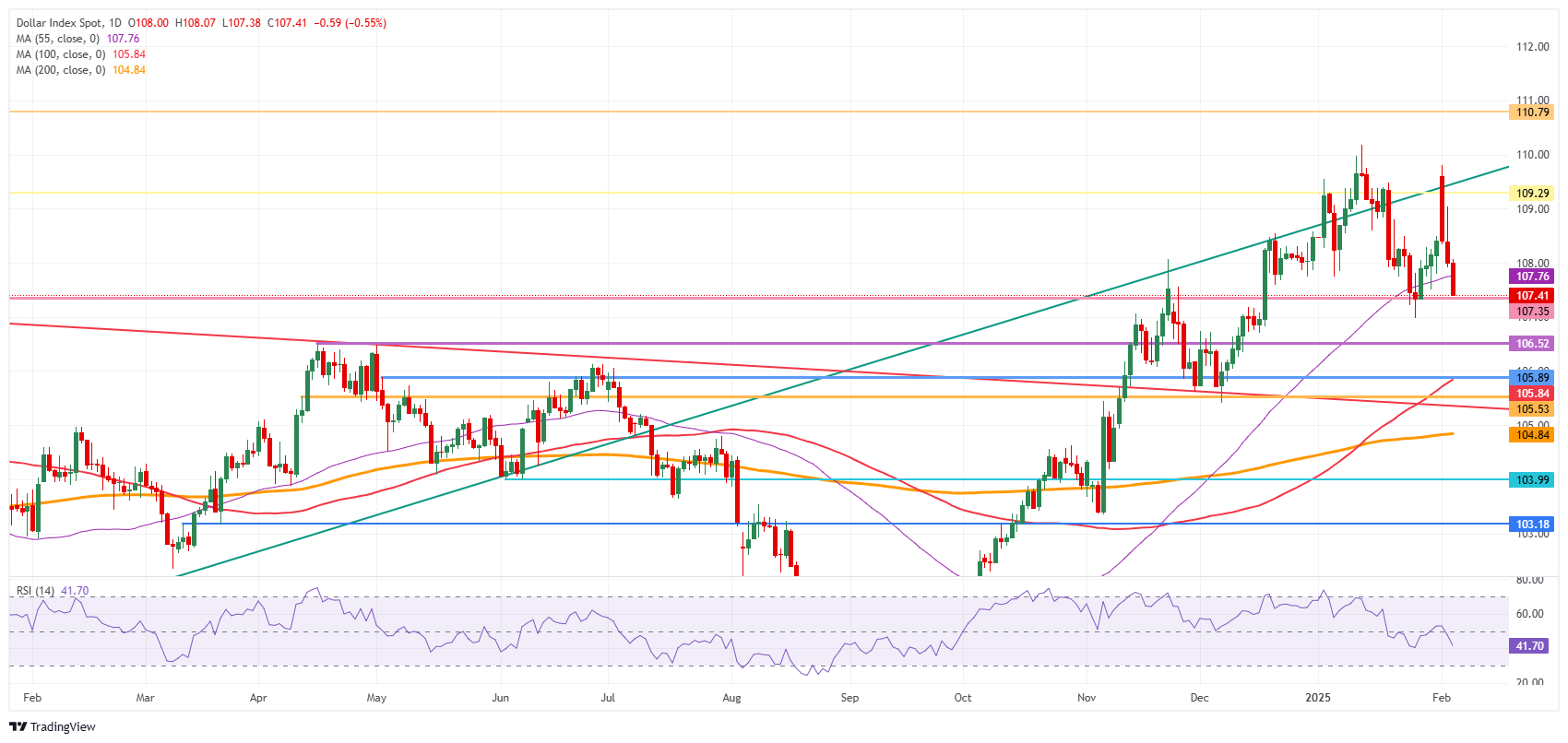
- The US Dollar Index (DXY) keeps testing major support at 107.35, which holds throughout the day.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the US Dollar against six major currencies, is at vital support in an otherwise downbeat trading session on Wednesday ahead of the US Purchase Managers Index (PMI) releases from both S&P Global and the Institute for Supply Management (ISM). Tensions in markets over the United States (US) President Donald Trump’s tariffs are unwinding now that levies on Mexico and Canada slapped over the weekend have been paused. This coincides with some US Dollar (USD) risk premium easing this Wednesday while Chinese traders head back to their desks after the Chinese New Year, with a surge in trading volumes.
As mentioned above, the economic data calendar shows a bulk of PMI releases on Wednesday. In Europe, the aggregate Eurozone, German, French, and Spanish PMI data have already been released earlier in the day, with final readings for January falling roughly in line to below their preliminary readings. In the US, S&P Global is set to release its reading in the early American session, with the ISM data specifically for the Services sector set to be issued just minutes thereafter.
Daily digest market movers: Difficult to read
- The ADP Employment Change for the private sector came in as a surprise increase to 183,000, beating the 150,000 expected new jobs in January compared to 122,000 previously.
- S&P Global revised up its final reading for the Services and Composite PMI for January. Services came in at 52.9 against 52.8 expected and the Composite at 52.7 against 52.4 in the previous reading.
- The ISM has released its January reading for the Services sector:
- Services PMI dips to 52.8, missing the 54.3 estimate and down from 54.1 in December.
- The Prices Paid component softens to 60.4, coming from 64.4 in the previous release.
- At 18:00 GMT, Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee delivers a speech on the current economy at the Chicago Fed’s 31st Annual Automotive Insights Symposium, held at the Bank’s Detroit Branch.
- Near 20:00 GMT, Federal Reserve Governor Michelle Bowman delivers a speech on Brief Economic Update and Bank Regulation at the 2025 Kansas Bankers Association Harold A. Stones Government Relations Conference.
- Equities mildy in the red, with the Nasdaq paring back earlier losses which stood at 1% at a given point.
- The CME FedWatch tool projects an 83.5% chance of the Fed keeping interest rates unchanged in the next meeting on March 19.
- The US 10-year yield is trading around 4.42%, bouncing of its fresh yearly low at 4.408%.
- Gold hits another fresh all-time high above $2,875, with investors fleeing equities and bonds, heading into bullion.
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Positioning is scrambled
The US Dollar Index (DXY) extends correction and dives lower on Wednesday. Traders and investors are heading to safe havens like Gold and the Swiss Franc (CHF). For once, the Greenback is not part of the rescue party, as risk-premium gained at the beginning of the week after President Trump slapped Mexico and Canada with tariffs over the weekend is starting to ease, no longer supporting an elevated US Dollar.
On the upside, the first barrier at 109.30 (July 14, 2022, high and rising trendline) was briefly surpassed but did not hold on Monday. Once that level is reclaimed, the next level to hit before advancing further remains at 110.79 (September 7, 2022, high).
On the downside, the October 3, 2023, high at 107.35 acts is trying to hold support and withstand the selling pressure this Wednesday. For now, that looks to be holding, though the Relative Strength Index (RSI) still has some room for the downside. Hence, look for 106.52 or even 105.89 as better levels.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
Central banks FAQs
Central Banks have a key mandate which is making sure that there is price stability in a country or region. Economies are constantly facing inflation or deflation when prices for certain goods and services are fluctuating. Constant rising prices for the same goods means inflation, constant lowered prices for the same goods means deflation. It is the task of the central bank to keep the demand in line by tweaking its policy rate. For the biggest central banks like the US Federal Reserve (Fed), the European Central Bank (ECB) or the Bank of England (BoE), the mandate is to keep inflation close to 2%.
A central bank has one important tool at its disposal to get inflation higher or lower, and that is by tweaking its benchmark policy rate, commonly known as interest rate. On pre-communicated moments, the central bank will issue a statement with its policy rate and provide additional reasoning on why it is either remaining or changing (cutting or hiking) it. Local banks will adjust their savings and lending rates accordingly, which in turn will make it either harder or easier for people to earn on their savings or for companies to take out loans and make investments in their businesses. When the central bank hikes interest rates substantially, this is called monetary tightening. When it is cutting its benchmark rate, it is called monetary easing.
A central bank is often politically independent. Members of the central bank policy board are passing through a series of panels and hearings before being appointed to a policy board seat. Each member in that board often has a certain conviction on how the central bank should control inflation and the subsequent monetary policy. Members that want a very loose monetary policy, with low rates and cheap lending, to boost the economy substantially while being content to see inflation slightly above 2%, are called ‘doves’. Members that rather want to see higher rates to reward savings and want to keep a lit on inflation at all time are called ‘hawks’ and will not rest until inflation is at or just below 2%.
Normally, there is a chairman or president who leads each meeting, needs to create a consensus between the hawks or doves and has his or her final say when it would come down to a vote split to avoid a 50-50 tie on whether the current policy should be adjusted. The chairman will deliver speeches which often can be followed live, where the current monetary stance and outlook is being communicated. A central bank will try to push forward its monetary policy without triggering violent swings in rates, equities, or its currency. All members of the central bank will channel their stance toward the markets in advance of a policy meeting event. A few days before a policy meeting takes place until the new policy has been communicated, members are forbidden to talk publicly. This is called the blackout period.
Information on these pages contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. Markets and instruments profiled on this page are for informational purposes only and should not in any way come across as a recommendation to buy or sell in these assets. You should do your own thorough research before making any investment decisions. FXStreet does not in any way guarantee that this information is free from mistakes, errors, or material misstatements. It also does not guarantee that this information is of a timely nature. Investing in Open Markets involves a great deal of risk, including the loss of all or a portion of your investment, as well as emotional distress. All risks, losses and costs associated with investing, including total loss of principal, are your responsibility. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of FXStreet nor its advertisers. The author will not be held responsible for information that is found at the end of links posted on this page.
If not otherwise explicitly mentioned in the body of the article, at the time of writing, the author has no position in any stock mentioned in this article and no business relationship with any company mentioned. The author has not received compensation for writing this article, other than from FXStreet.
FXStreet and the author do not provide personalized recommendations. The author makes no representations as to the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of this information. FXStreet and the author will not be liable for any errors, omissions or any losses, injuries or damages arising from this information and its display or use. Errors and omissions excepted.
The author and FXStreet are not registered investment advisors and nothing in this article is intended to be investment advice.